The calorific value of biogas is about 6 kWh/m3 - this corresponds to about half a litre of
diesel oil. The net calorific value depends on the efficiency of the burners or appliances.
Methane is the valuable component under the aspect of using biogas as a fuel.
Utilization
The history of biogas utilization shows independent developments in various developing and
industrialized countries. The European biogas-history and that of Germany in particular, as
well as developments in Asian countries form the background of German efforts and
programmes to promote biogas technology worldwide.
Normally, the biogas produced by a digester can be used as it is, just in the same way as
any other combustible gas. But it is possible that a further treatment or conditioning is
necessary, for example, to reduce the hydrogen-sulfide content in the gas. When biogas is
mixed with air at a ratio of 1:20, a highly explosive gas forms. Leaking gas pipes in enclosed
spaces constitute, therefore, a hazard. However, there have been no reports of dangerous
explosions caused by biogas so far.
A first overview of the physical appearance of different types of biogas plants describes the
three main types of simple biogas plants, namely balloon plants, fixed-dome plants and
floating-drum plants.
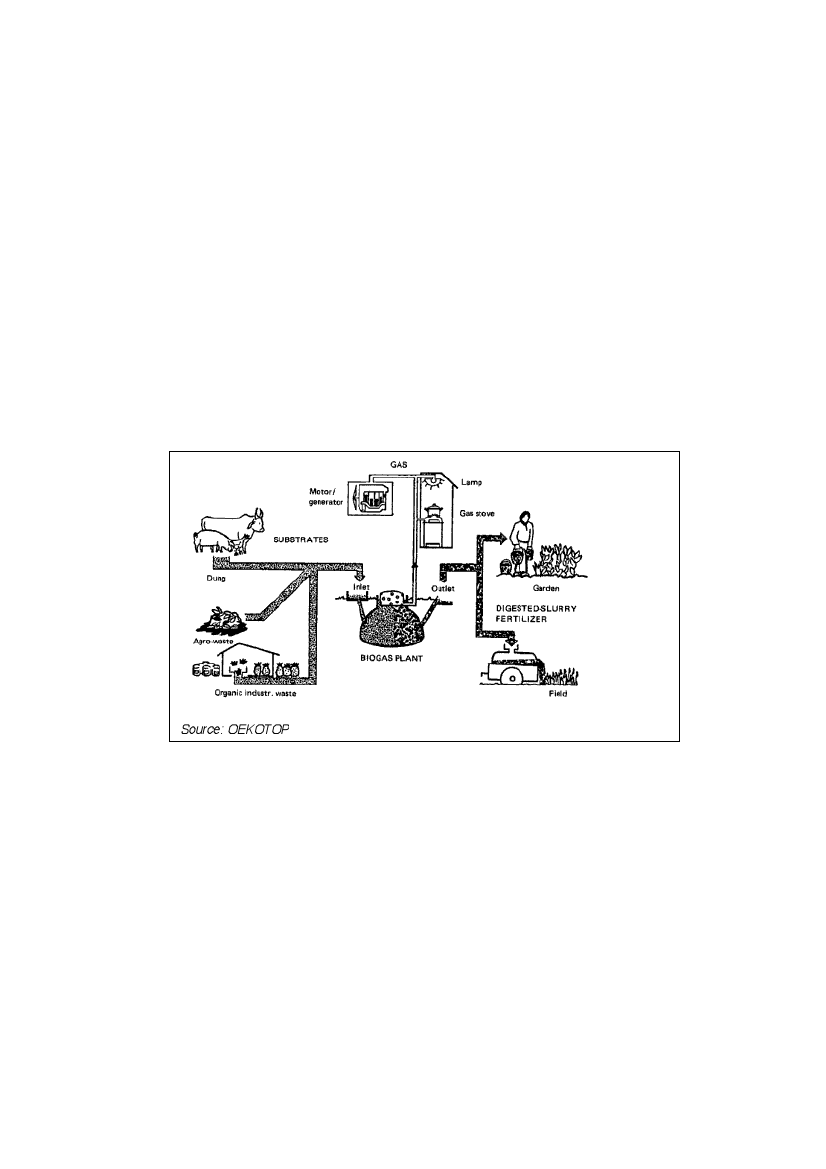
Figure 1: A typical biogas system configuration
Source: OEKOTOP
The Benefits of Biogas Technology
Well-functioning biogas systems can yield a whole range of benefits for their users, the
society and the environment in general:
• production of energy (heat, light, electricity) ;
• transformation of organic waste into high quality fertilizer;
• improvement of hygienic conditions through reduction of pathogens, worm eggs and
flies;
• reduction of workload, mainly for women, in firewood collection and cooking.
• environmental advantages through protection of soil, water, air and woody vegetation;
• micro-economical benefits through energy and fertilizer substitution, additional
income sources and increasing yields of animal husbandry and agriculture;
• macro-economical benefits through decentralized energy generation, import
substitution and environmental protection
5